The scale of that crisis has been highlighted by a new OECD report which shows just how much bulging waistlines are costing health systems around the world.
Obese people tend to avail of healthcare services more frequently with a higher rate of specialty care visits, inpatient stays and surgery, all leading to higher healthcare spending. The OECD states that obese people have 2.4 times more prescriptions than healthy-weight individuals on average while hospital stays are longer and require more expensive and complex treatment.
For example, obesity is responsible for 70 percent of all treatment costs for diabetes, 23 percent of treatment costs for cardiovascular diseases and 9 percent for cancers. On average, treating diseases caused by excess weight costs 8.4 percent of total health spending in OECD nations.
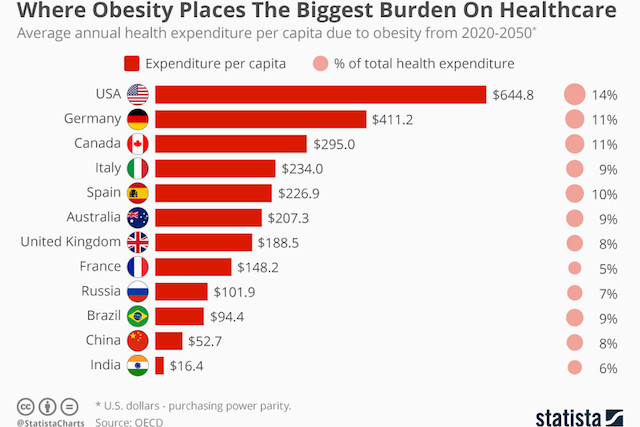
So where is the financial burden highest? Unsurprisingly, perhaps, the U.S. has to spend the most battling the bulge. Obesity is expected to cost the health system $644 per capita annually from 2020 to 2050 - 14 percent total American health expenditure.
By comparison, Canada will ‘only’ have to spend $295 each year during the same period which equates to 11 percent of its total health spending.
Luxembourg ranked 6th out of 53 countries in the study, with annual per capita expenditure on obesity projected at $303, or about 8% of GDP.
The EU28 average was forecast at $195 per capita, or about 9% of GDP.